Neighborhood Planning For Green Stormwater Infrastructure
Step 4 of 6: Stormwater Site Analysis
After a neighborhood has compiled a list of potential GSI sites based on Project Criteria and Project Types, it is helpful to conduct a preliminary stormwater site analysis.
The stormwater site analysis is not a necessary step in the Neighborhood Planning Input process. However, it is recommended that the organization developing the neighborhood plan conduct at least one or two stormwater site analyses in order to understand how basic stormwater management feasibility is determined for a site. If the neighborhood would like to begin developing a concept plan for a site, this information will inform where a potential GSI project could be located.
After the neighborhood planning input submission has been received, PWD’s stormwater engineers will conduct a full analysis of all recommended sites, including utility conflicts and drainage area calculations, to determine whether this site qualifies for a green infrastructure stormwater management project.
1. Site Inventory
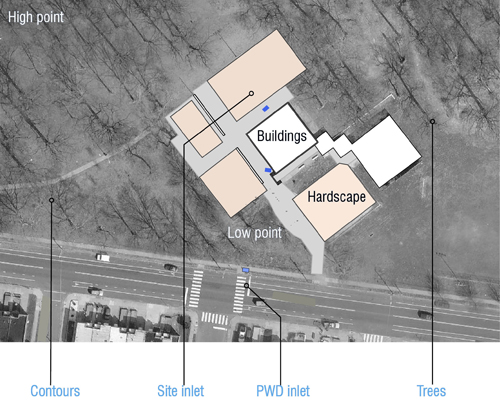 |
Find or draw a map of your site. To find an aerial photograph of your site, go to GoogleMaps, type in the address or intersection of your site, and set the map view to “Satellite.” Identify all vegetation, buildings, property lines, impervious areas (hard or paved surfaces), high and low points and stormwater inlets. Stormwater inlets are a necessary element since all green infrastructure systems must be connected via an overflow pipe to an existing inlet. |
2. Drainage Areas
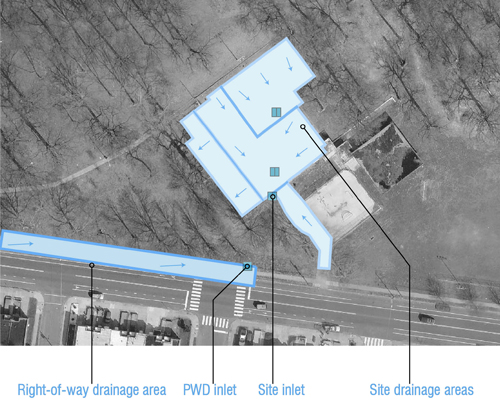 |
Look at the contours (topography) of the land to determine the high and low points of the site. It can be helpful to visit the site after a rain event. Draw arrows on all of the impervious surfaces on your map, showing the low points or inlets where the stormwater drains to, both on your site and on the streets. These are your drainage areas. Projects should attempt to maximize the drainage areas that they propose to manage. |
3. Identify locations for Green Stormwater Infrastructure (GSI)
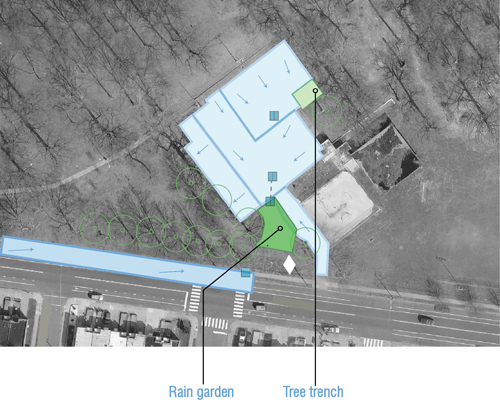 |
GSI should be located adjacent to inlets, at the lowest points of the site. GSI is typically rain gardens, tree trenches, or other types of planters that capture runoff and allow it to infiltrate into the ground. It can also be pervious pavement. Avoid locating GSI within an area of healthy, mature trees or within 10 feet of any structure. For more detailed instructions on stormwater analysis, view Site Design for Stormwater Management. |
Continue to Step 5. Gathering Information